In addition, the consistency principle of accounting calls for a consistent accounting method or policy for an entity. Without a consistent approach, the financial results would be meaningless and could be easily manipulated. For example, any cost accountant would adjust the asset depreciation to adjust the period profits showing unrealistic profitability. The Principle of Materiality is pivotal in financial reporting and accounting under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are uniform accounting principles for private companies and nonprofits in the U.S.
- The consistency principle is important in accounting because it ensures that financial statements are comparable from one period to another.
- Apart from recording, the other half of accounting practice summarizing is equally important too.
Application and Examples: GAAP Principle of Continuity
However, the change and its effects must be clearly disclosed for the benefit of the readers of the financial statements. In year 3, Bob’s income is extremely loan and Bob is trying to show a profit to get another bank loan. Bob can make a justifiable change in accounting method like in the first example, but he cannot switch back and forth year after year.
Revenue Recognition Principle
However, the amount of the expense is so small that no reader of the financial statements will be misled if you charge the entire $100 to expense in the current period, rather than spreading it over the usage period. In fact, if the financial statements are rounded to the nearest thousand or million dollars, this transaction would not alter the financial statements at all. This was disclosed, as required by GAAP, in the footnotes to the audited financial statements. Consistency concept is important because of the need for comparability, that is, it enables investors and other users of financial statements to easily and correctly compare the financial statements of a company. The concept of consistency means that accounting methods once adopted must be applied consistently in future.
What does Consistency Principles of Accounting mean?
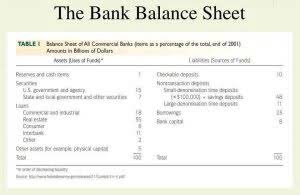
The consistency principle in accounting refers to the practice of using the same accounting methods, principles, and policies from one accounting period to another. It ensures that financial statements are comparable and reliable over time, allowing stakeholders to make meaningful comparisons and assessments of a company’s financial performance. Basically, the convention of consistency refers to consistent use of accounting principles in a company or business entity. Typically, in the balance sheet of each entity, it contains several assets and liabilities.

For example, if a company purchases a vehicle, the cost of the vehicle is spread over its estimated useful life rather than being fully expensed in the year of purchase. In that case, the Principle of Prudence requires that an estimated loss be recorded in the financial statements. In this case, the entity should apply with IAS 8 whether it is a retrospective or prospective change.
What is Going Concerned? Definition, Assessment, Indicators, Example, Disclosure
The first is that there is no legal differentiation between Andrea and her business. Following from that, Andrea will be personally responsible for any debts that the business incurs, and her income statement accounts personal assets may be used to settle business debts. As FA2 only relates to unincorporated businesses (sole traders and partnerships), this might seem like an unrealistic differentiation.
If everyone reported their financial information differently, it would be difficult to compare companies. Accounting principles set the rules for reporting financial information, so all companies can be compared uniformly. The materiality principle states that an accounting standard can be ignored if the net impact of doing so has such a small impact on the financial statements that a reader of the financial statements would not be misled. Under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), you do not have to implement the provisions of an accounting standard if an item is immaterial.
This definition does not provide definitive guidance in distinguishing material information from immaterial information, so it is necessary to exercise judgment in deciding if a transaction is material. When accounting principles allow a choice among multiple methods, a company should apply the same accounting method over time or disclose the change in its accounting method in the footnotes of the financial statements. In a complex and large business, the selection of accounting principles such as inventory costing methods can put huge effects on financial results. On the flip side, cost accountants can also use the lack of consistency to showcase favorable accounting results and increased profits. The practical implications of not following the consistency principle can be calamitous for the company.
Business Entity Concept – is the idea that the business and the owner of the business are separate entities and should be accounted for separately. Historical Cost Principle – requires companies to record the purchase of goods, services, or capital assets at the price they paid for them. Assets are then remain on the balance sheet at their historical without being adjusted for fluctuations in market value. Theoretically, there are a number of bases that could be used to derive the value at which transactions are recorded. However, historical cost is the only one of these that needs to be considered in the context of FA2. As she is a sole trader (ie her business is unincorporated), there are some important legal points to be noted.